Commercial Gold Mining In Lapland Finland
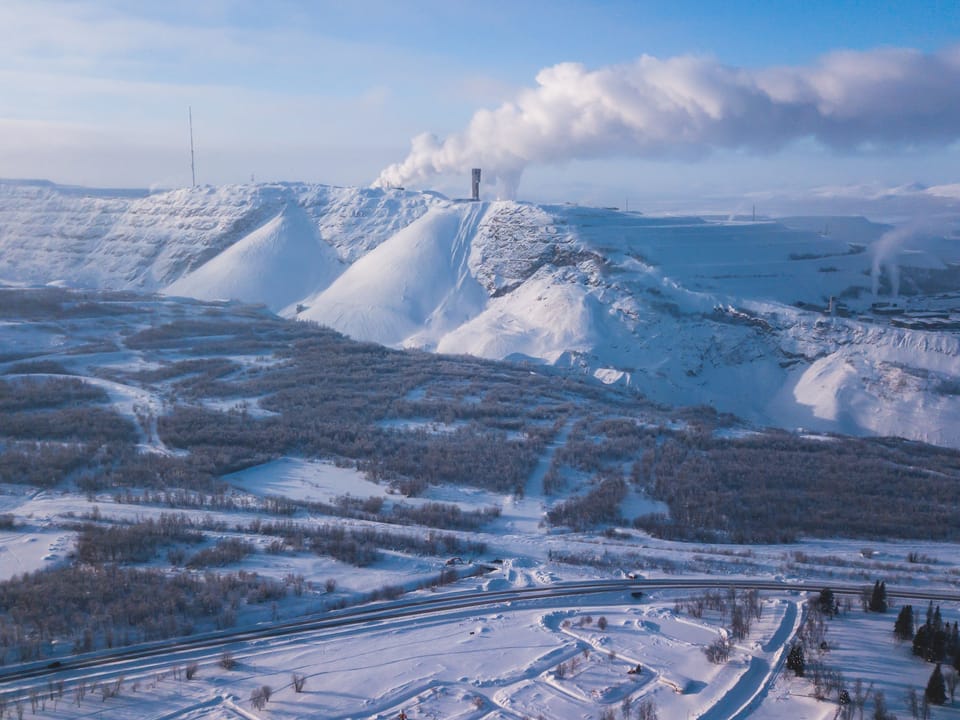

Lapland, Finland's northernmost region, has emerged as a promising frontier for commercial gold mining. With its rich mineral deposits, established infrastructure, and supportive regulatory environment, Lapland has attracted both major mining companies and junior explorers. This article explores the key gold mining operations, economic impact, and future prospects of the industry in this resource-rich area.
Gold Production in Lapland (kg)
Lapland's Significance in European Gold Production
Lapland plays a crucial role in European gold production, making Finland one of the continent's leading gold producers:
- Finland is the largest gold producer in the European Union, with an output of 8,000 kilograms (256,000 ounces) in 2016.
- Lapland is home to the Kittilä mine, the largest gold mine in Europe, which produced over 200,000 ounces of gold in 2020.
- The Kittilä mine alone contributed around 5,500 kilograms (176,000 ounces) to Finland's total gold production in 2016.
- The Central Lapland Greenstone Belt, extending into Lapland, is a major gold-producing region. It hosts two significant gold mines - Kittilä and Pahtavaara, with the latter producing almost 450,000 ounces over 16 years.
- Lapland accounts for over 40% of Finland's total metal ore mining operations turnover and mining support service activities turnover.
- The region's share of nationwide metal refining activities is almost 40%.
These figures underline Lapland's importance not just to Finland's mining sector, but to gold production across Europe.
Key Gold Mining Operations
1. Agnico Eagle's Kittilä Mine
The Kittilä Mine, operated by Agnico Eagle Finland, stands as Europe's largest gold mine. In production since 2009, it's renowned for its high-grade gold deposits. Some key points about the Kittilä Mine include:
- Produced over 200,000 ounces of gold in 2020
- Ongoing €160 million investment to enhance operations and increase production capacity
- Significant contributor to Finland's gold output
- Employs up to 960 people including subcontractors, making it the largest employer among Lapland's mines
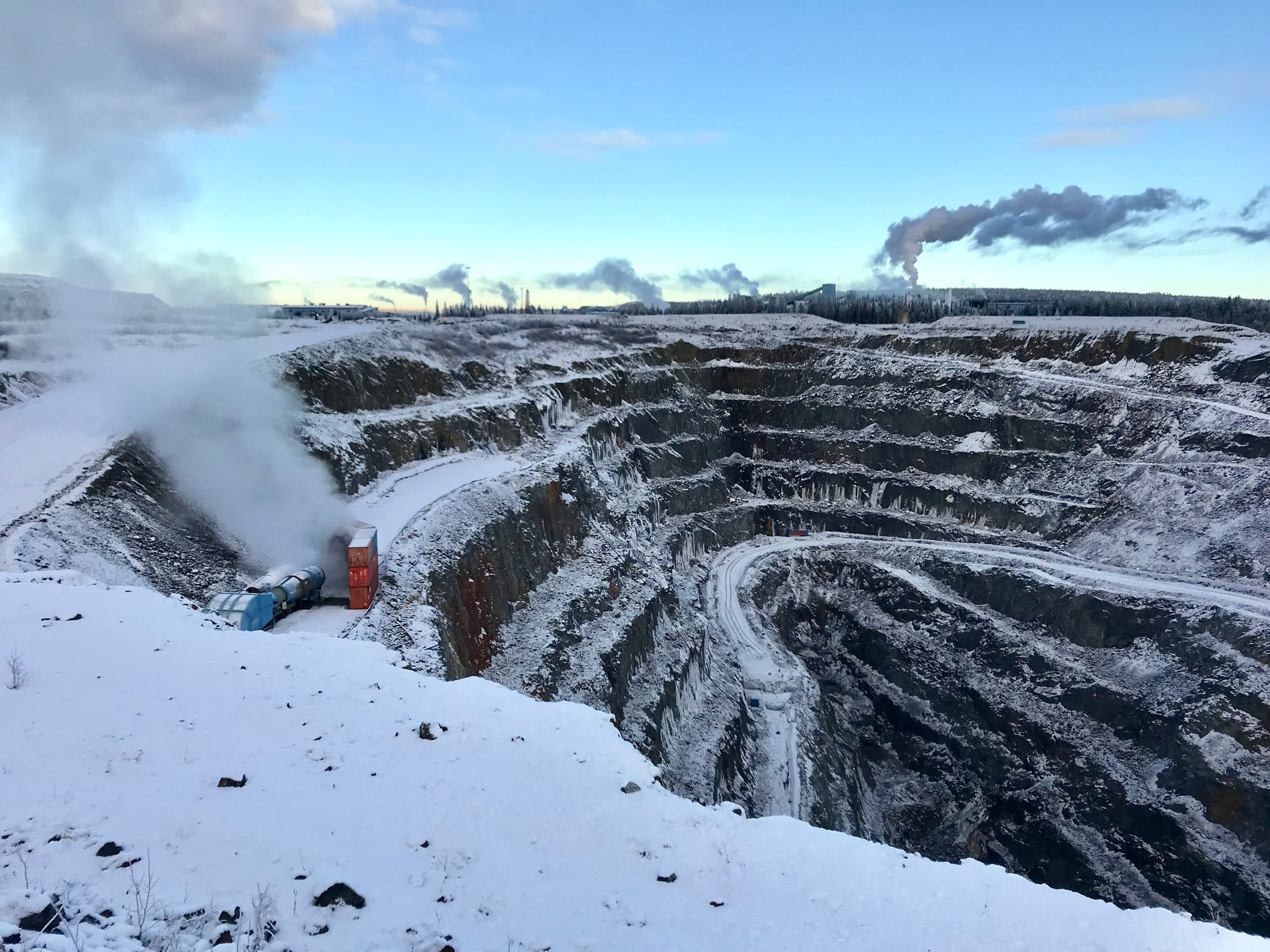

2. Rupert Resources - Rupert Lapland Project
Rupert Resources is focused on the Rupert Lapland Project, which includes:
- The Ikkari gold discovery, a multi-million ounce gold occurrence
- The Pahtavaara mine
- Located within the mineral-rich Central Lapland Greenstone Belt
- Ongoing exploration to identify additional resources
3. Boliden's Kevitsa Mine
While primarily a copper-nickel operation, Boliden's Kevitsa Mine also produces gold as a byproduct. Notable aspects include:
- One of Finland's largest mines by total quarrying volume
- Employs around 800 people
- Undergoing €80 million upgrades to enhance its concentration plant
4. Emerging Projects
Several promising projects are in various stages of development:
- AA Sakatti Mining Oy's Sakatti project: Focused on copper and nickel with significant gold potential
- Hannukainen Mining Oy: Aiming to establish an open quarry for iron, gold, and copper in Kolari
- Mawson Resources' Rompas-Rajapalot project: Targeting gold and cobalt in the Ylitornio and Rovaniemi areas
Economic Impact and Future Prospects
The mining sector plays a crucial role in Lapland's economy:
- In 2018, it provided approximately 1,700 person-years of employment
- Total turnover of around €550 million in 2018
- Expected continued growth supported by Finland's favorable mining policies
Junior Mining Companies Exploring Gold in Lapland, Finland
Lapland has become a hotspot for junior mining companies seeking new gold deposits. The area's rich geological formations, particularly in the Central Lapland Gold Belt (CLGB), combined with Finland's favorable mining policies and stable political environment, make it an attractive destination for exploration.
Overview of Mining in Lapland
Lapland's mining sector benefits from several advantages:
- Rich mineral deposits, especially in the Central Lapland Gold Belt
- Favorable mining policies and a stable political environment
- Well-established infrastructure
- Government support for sustainable mining practices
- Finland's commitment to environmental responsibility
These factors have attracted numerous junior mining companies, primarily from Canada, to explore and develop potential gold deposits in the region.
Key Junior Mining Companies in Lapland
1. FireFox Gold Corp.
FireFox Gold is a Canadian junior mining company that has established a strong presence in the Central Lapland Gold Belt.
Key Projects:
- Risti Project: Shows promising gold mineralization and is located near existing gold mines
- Launi Project: Another area where FireFox is conducting extensive exploration activities
Strategy: FireFox aims to leverage its land position and geological expertise to discover new gold deposits, utilizing modern exploration techniques.
2. Aurion Resources
Aurion Resources, another Canadian company, focuses on gold exploration in northeastern Finland.
Key Projects:
- Aamurusko Project: Located in the heart of the CLGB, showing potential for high-grade gold deposits
- Kuhmo Project: Targets both gold and critical minerals, enhancing the company's portfolio
Strategy: Aurion is committed to aggressive exploration and has been successful in attracting investment due to its promising land holdings and strategic partnerships.
3. Gemdale Gold Inc.
Gemdale Gold is a junior mining company with a particular interest in the Central Lapland Gold Belt.
Key Projects:
- Sirrka Extension Project: Aims to expand the known mineralization in the area
- Pontio Project: Another exploration site showing potential for gold deposits
Strategy: Gemdale focuses on utilizing innovative exploration techniques to maximize resource identification and development.
4. Mawson Resources
Mawson Resources is engaged in exploration activities targeting both gold and cobalt in Finland.
Key Projects:
- Rompas-Rajapalot Project: Notable for its high-grade gold and cobalt mineralization, located in the Ylitornio and Rovaniemi areas
Strategy: Mawson is advancing its projects through drilling and resource estimation, aiming to establish a significant mineral resource base.
5. AA Sakatti Mining Oy
While not strictly a junior mining company, AA Sakatti Mining Oy, a subsidiary of Anglo American, is worth mentioning due to its significant presence in Lapland.
Key Projects:
- Sakatti Project: Primarily a copper-nickel exploration initiative, currently in the environmental impact assessment phase
Strategy: The company is working closely with local communities and stakeholders to ensure sustainable development and minimize environmental impact.
Opportunities and Challenges
The junior mining sector in Lapland faces both opportunities and challenges:
Opportunities:
- Increasing global demand for gold and critical minerals
- Significant foreign investment interest
- Technological advancements enhancing exploration capabilities
Challenges:
- Balancing mining activities with environmental sustainability
- Navigating complex permitting processes and ensuring compliance with Finnish regulations
- Engaging effectively with local communities and stakeholders
The Future of Junior Mining in Lapland
The future looks promising for junior mining companies in Lapland. The region's geological potential, combined with supportive government policies, positions Finland as a key player in the European mining landscape. As these companies advance their projects, they contribute not only to the local economy but also to the broader mining industry in Finland and Europe.
The focus on sustainable practices and community engagement will likely play a crucial role in the success of these junior mining companies. As global demand for gold and critical minerals continues to grow, particularly in the context of the green energy transition, Lapland's mining sector is poised for significant growth and development.
Lapland, Finland, has emerged as a vibrant hub for junior mining companies, particularly in the gold exploration sector. The combination of rich geological resources, supportive policies, and a commitment to sustainable practices makes the region an attractive destination for these companies. As exploration efforts continue and projects advance, Lapland's junior mining sector is set to play an increasingly important role in the European mining industry, contributing to both local economic development and global mineral supply.
The Central Lapland Greenstone Belt: A Geological Treasure Trove
The Central Lapland Greenstone Belt (CLGB) is a remarkable geological formation located in northern Finland. Known for its rich mineral deposits, particularly gold, this region has become a focal point for mining and exploration activities, offering significant economic potential and geological interest.
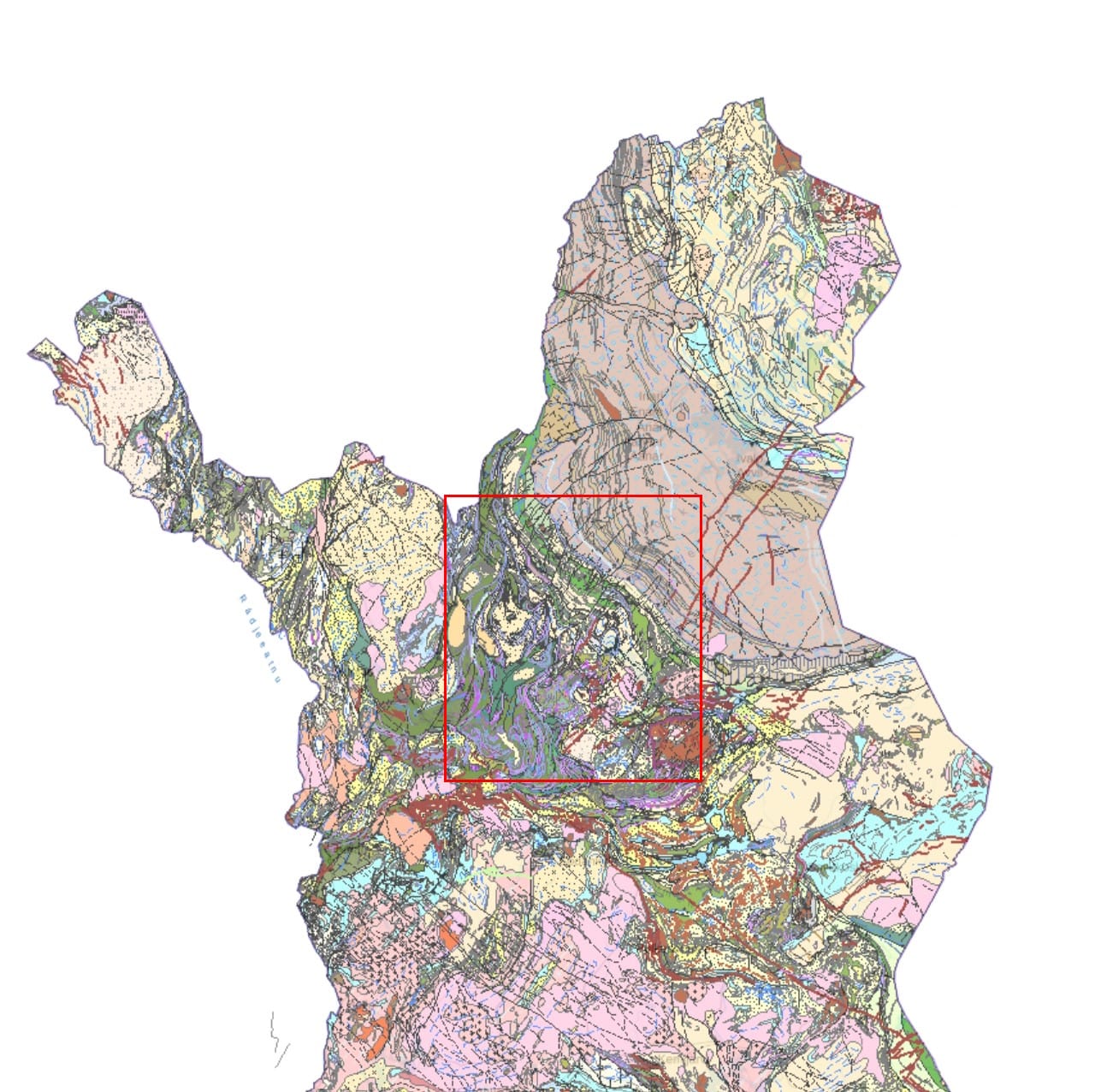
Geological Overview
Formation and Age
The CLGB is primarily composed of Paleoproterozoic rocks, dating back approximately 2.5 billion years. This ancient geological history contributes to the complexity and richness of the mineral deposits found in the area.
Composition
The belt consists mainly of metamorphosed volcanic and sedimentary rocks, including:
- Basalts: Foundational volcanic rocks formed from lava flows
- Andesites: Intermediate volcanic rocks indicating varied volcanic activity
- Sedimentary Sequences: Various types of sedimentary rocks altered through metamorphism
Tectonic History
The CLGB has undergone a complex tectonic history characterized by multiple deformation events:
- D1 (1.92-1.90 Ga): Initial thrust faulting during east-west contraction
- D2 (1.90-1.89 Ga): North-south shortening
- Subsequent Phases (D3 to D5): Changes in stress regimes, leading to the development of shear zones critical for mineralization
Mineralization and Common Minerals
The CLGB is renowned for its diverse mineral resources. The most common minerals and deposits include:
- Gold: Primarily found in orogenic gold deposits along shear zones
- Copper: Often associated with other base metals
- Nickel: Commonly found in association with ultramafic rocks
- Cobalt: Usually present alongside nickel and copper deposits
- Platinum Group Metals (PGMs): Including platinum and palladium
- Iron-Oxide-Copper-Gold (IOCG) Deposits: Characterized by the presence of iron oxides along with copper and gold
- Chromite: Adding to the mineral diversity of the region
- Phosphorus: Indicating potential for agricultural and industrial applications
- Other minerals: Including graphite, garnet, hornblende, and biotite
Economic Significance
The CLGB plays a crucial role in Finland's mining sector and overall economy:
- Home to the Kittilä Mine, the largest gold mine in Europe, producing approximately 175,000 ounces of gold annually
- Hosts several active mining operations and exploration projects
- In 2018, mining and quarrying operations in Lapland provided about 1,700 person-years of employment
- The sector had a turnover of around €550 million in 2018
Current Mining Operations
Several notable mining operations are active in the CLGB:
- Kittilä Mine: Operated by Agnico Eagle, it's Europe's largest gold mine
- Rupert Resources: Focused on the promising Ikkari gold deposit
- Other Projects: Companies like FireFox Gold and Mawson Resources are actively exploring various properties within the CLGB
Future Prospects
The CLGB is poised for growth, driven by several factors:
- Geological Potential: The region remains largely underexplored compared to other global gold mining regions
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in exploration technologies are enhancing the ability to identify and develop mineral resources
- Supportive Regulatory Environment: Finland's stable political climate and transparent mining policies make the CLGB an attractive destination for investment
The Central Lapland Greenstone Belt stands as a geological treasure trove, offering rich mineral deposits and significant economic potential. Its complex geological history, diverse mineralization, and ongoing exploration activities position it as an increasingly important player in the global mining industry. As technology advances and demand for minerals grows, particularly in the context of green energy transition, the CLGB is likely to remain a focal point for both junior and major mining companies in the years to come.
The Economic Impact of Mining in Lapland, Finland
Mining in Lapland plays a crucial role in shaping the local economy. Let's explore the various ways in which mining activities contribute to economic growth, job creation, and infrastructure development, while also addressing the challenges and considerations associated with this industry.
Positive Economic Contributions
1. Job Creation
Mining is a significant source of employment in Lapland:
- As of 2018, the mining sector accounted for 44% of all employment in Finland's extractive and ore concentration sector.
- Approximately 3,800 direct jobs exist within the mineral cluster, which includes mining, metal refining, and related services.
- When considering indirect employment effects, the mining sector supports around 21,431 person-years of employment in Lapland.
- This includes jobs in subcontracting, local services, and businesses catering to the mining workforce.
- New projects, such as the Sakatti Project, are expected to create additional jobs, with estimates of 350-400 new positions once operational.
2. Infrastructure Development
Mining operations often lead to significant improvements in local infrastructure:
- Development of roads, transportation networks, and utilities.
- These improvements benefit not only mining companies but also local residents and other industries, including tourism.
- Enhanced access to remote areas can make them more attractive for tourism and other economic activities.
3. Economic Diversification
The mining industry provides an alternative to traditional economic activities in Lapland:
- Offers diversification from industries like tourism and forestry.
- Helps stabilize local economies, especially in smaller communities that may be heavily reliant on a single industry.
- Can help mitigate unemployment rates, particularly among young people, by providing stable job opportunities.
4. Investment and Economic Growth
Mining brings significant investment to the region:
- Planned investments for new projects total over four billion euros.
- This influx of capital stimulates local economies and creates a multiplier effect, benefiting various sectors.
- Supports local businesses such as construction firms, service providers, and suppliers.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Environmental Concerns
While mining brings economic benefits, it also poses environmental challenges:
- Potential for habitat destruction, pollution, and resource depletion.
- Can affect local ecosystems and the quality of life for residents.
- Balancing mining activities with environmental sustainability is crucial.
- Implementation of sustainable mining practices is essential to minimize negative impacts.
2. Community Relations
Effective engagement with local communities is vital:
- Mining companies must address concerns and ensure equitable sharing of benefits.
- Some residents may have mixed feelings about mining, weighing economic benefits against potential environmental and social impacts.
- Effective communication and collaboration are essential for maintaining positive relationships with residents.
3. Long-Term Economic Viability
The sustainability of economic benefits depends on several factors:
- Viability of mineral deposits and global demand for minerals.
- Once a deposit is exhausted, communities may face economic challenges if they have not diversified their economies.
- Planning for post-mining economic transitions is crucial for long-term community sustainability.
Conclusion
Mining in Lapland plays a pivotal role in shaping the local economy, providing jobs, infrastructure, and opportunities for economic diversification. While the sector presents significant benefits, it also requires careful management to address environmental concerns and ensure that the economic gains are sustainable over the long term. Balancing the interests of mining, local communities, and environmental stewardship will be key to realizing the full potential of Lapland's rich mineral resources and ensuring a prosperous future for the region.